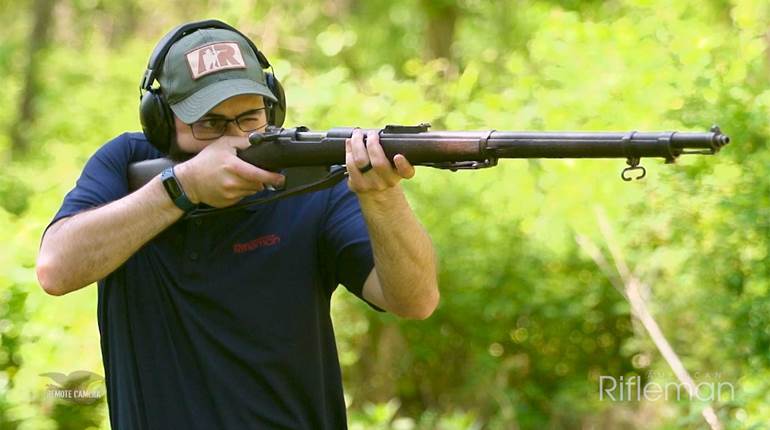
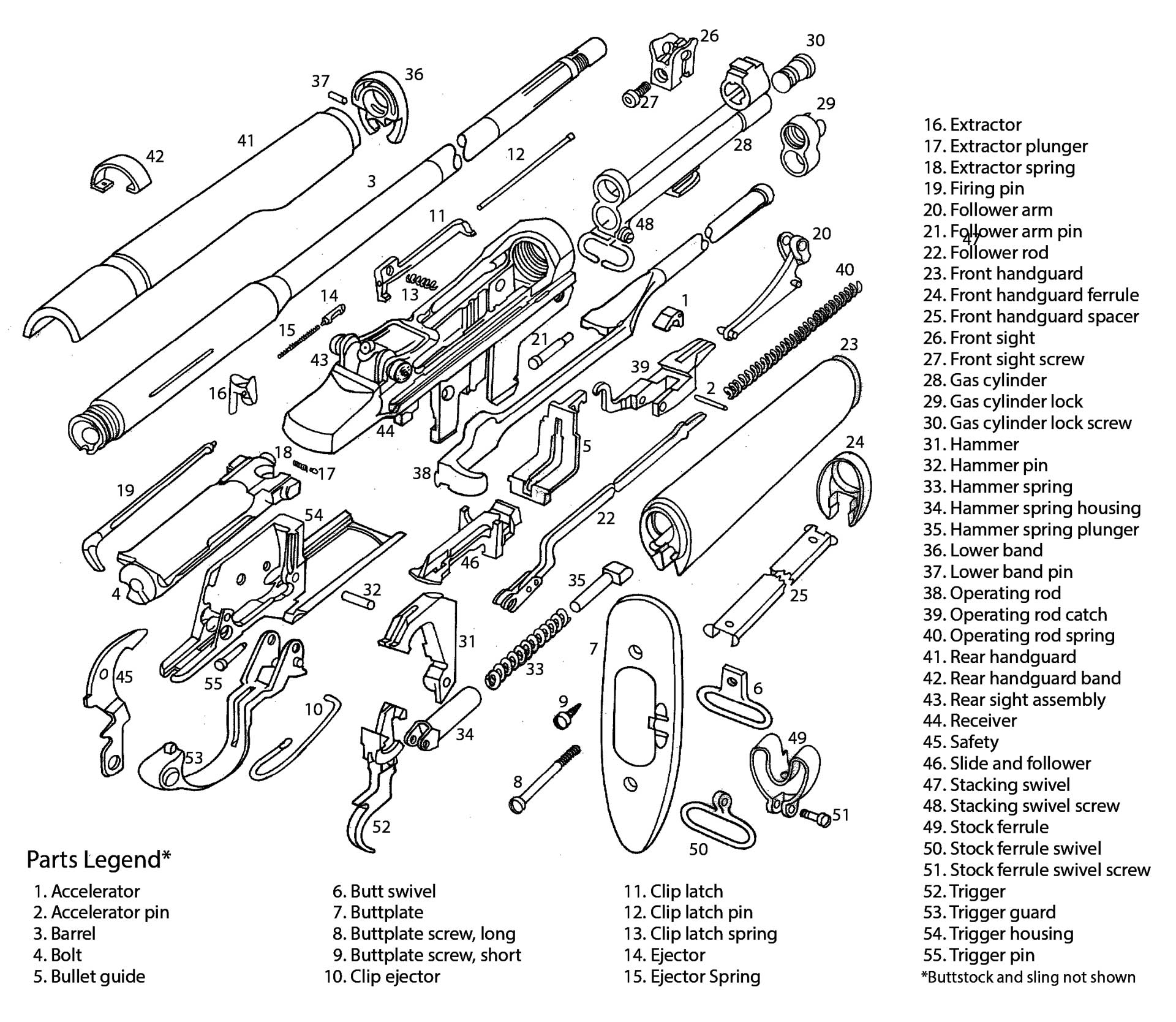
A History of the M1 Garand
During World War I, the United States Army experimented with a number of different machine gun designs, and the news reports of the tests got a young inventor thinking about, and eventually designing, a machine gun of his own. His initial attempt was a primer-actuated light machine gun he submitted to the National Bureau of Standards, which had instructed him to make a model of it. That design became the basis for what would, eventually, become the M1 rifle—commonly called the “Garand” after its inventor, John Cantius Garand.
Garand, who became a Springfield Armory employee in 1919, had an extensive background in design and production. Once at Springfield, he was tasked with designing a semi-automatic shoulder rifle based upon his earlier machine gun. He worked on and improved the design for the next 17 years. The now-familiar M1 was finally adopted on January 9, 1936, the rifle was adopted as the “U.S. Rifle, Cal. .30, M1.”
Early production rifles used a “gas trap” instead of the later “gas port” design and initially did not perform as well as expected, but once the “bugs” were worked out, the rifle was favorably received. It was fed by an eight-round en-bloc clip that was ejected along with the last spent casing, locking the bolt back and leaving the receiver open for a fresh clip to be inserted. User-friendly, accurate and chambered for the powerful .30-’06 Sprg. cartridge, the M1 gained a reputation as a hardy and well-made service rifle.
World War II was the rifle’s baptism of fire, and it performed admirably. To a man, the G.I.s put their faith in their M1 rifles and took them from North Africa to Okinawa. Along the way, Garand made more improvements to the rifle based upon field experience and soldiers’ comments.
Although late to adopt the rifle, the Marines liked it, too, and found it well-suited for jungle fighting. America was the only country to equip its fighting men with a semi-automatic rifle as a standard shoulder arm. The venerability of the rifle was further established in the Korean War.
The M1 rifle is not without faults. At just under 10 lbs. it is heavy and the en-bloc clip does not allow for easy “topping off.” Because of those drawbacks, America sought a high-capacity, fully automatic rifle for individual soldiers. Reliability and accuracy were paramount, however, and the M1 was the measuring stick. What later became the M14 was based upon the M1.
Combined, Springfield Armory and Winchester Repeating Arms manufactured more than 4 million M1s during World War II. International Harvester and Harrington & Richardson manufactured them as well, and, during the Korean War, more than 500,000 were made.
The rifle is considered one of the finest ever produced by American armories. Its popularity is evidenced by its representation on the firing line at Camp Perry and other highpower rifle matches to this day. It is accurate, robust and its service record speaks for itself.
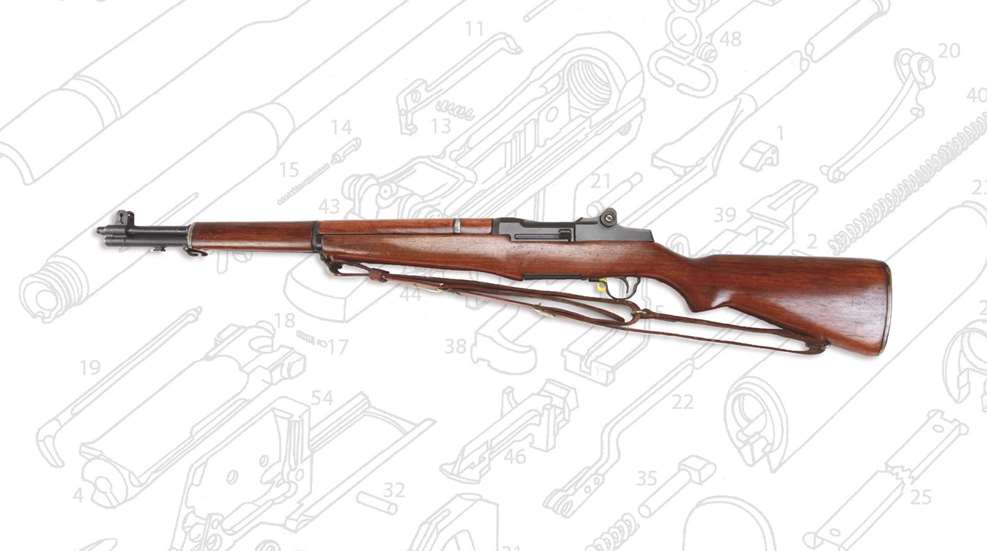
Disassembly
Disassembly of the unloaded M1 rifle begins by pulling the bolt rearward until it locks back. Visually inspect the chamber to ensure it is not loaded, then press down on the slide and follower while holding the operating rod and ease the bolt forward. Do this carefully or you will end up with a case of “M1 thumb”—a highly unpleasant condition!
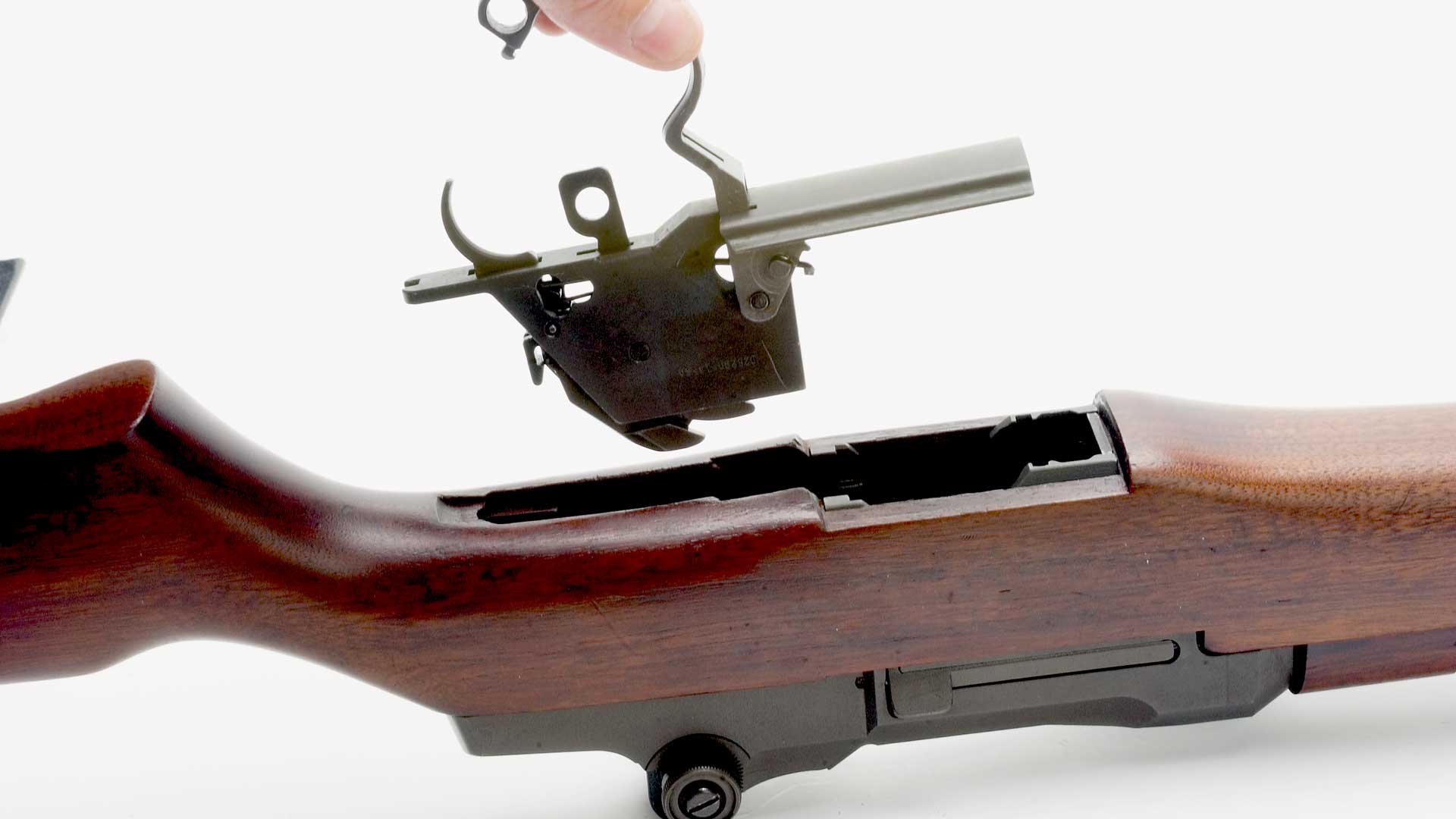

Once this is done, disassembly can begin. Pull rearward on the trigger guard (53) and then out and away from the stock. The entire trigger housing (54) and assembly will separate from the rifle (Fig. 1). Lift the receiver (44) and assembly away from the stock.
Disengage the follower rod (22) from the follower arm (20) by moving the rod toward the muzzle. Remove the rod and operating rod spring (40). Next, push out the follower arm pin (21) from the receiver’s left side. Then lift away the bullet guide (5),
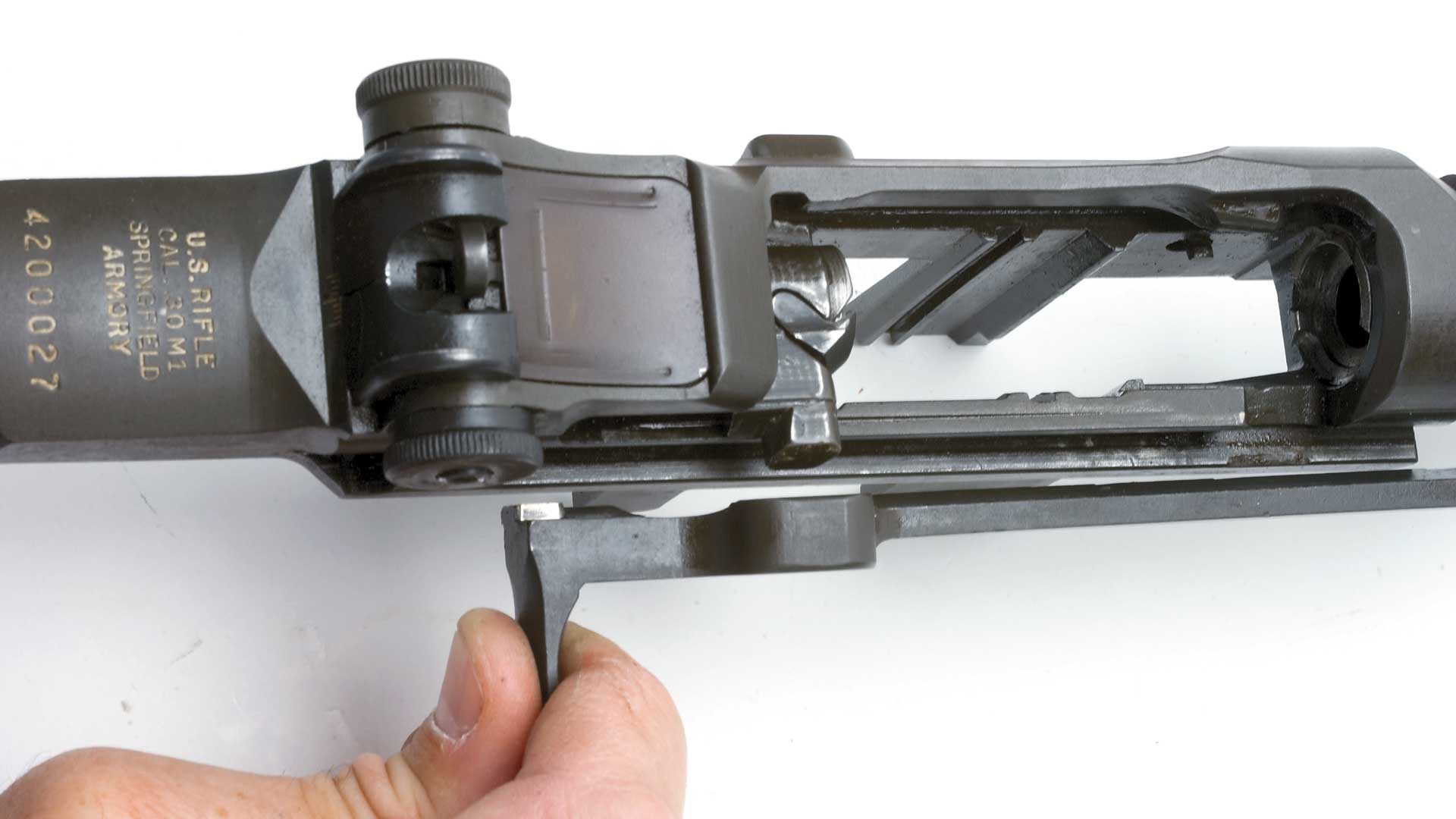
follower arm and operating rod catch (39) (Fig. 2). Reach down into the receiver and lift out the slide and follower (46).
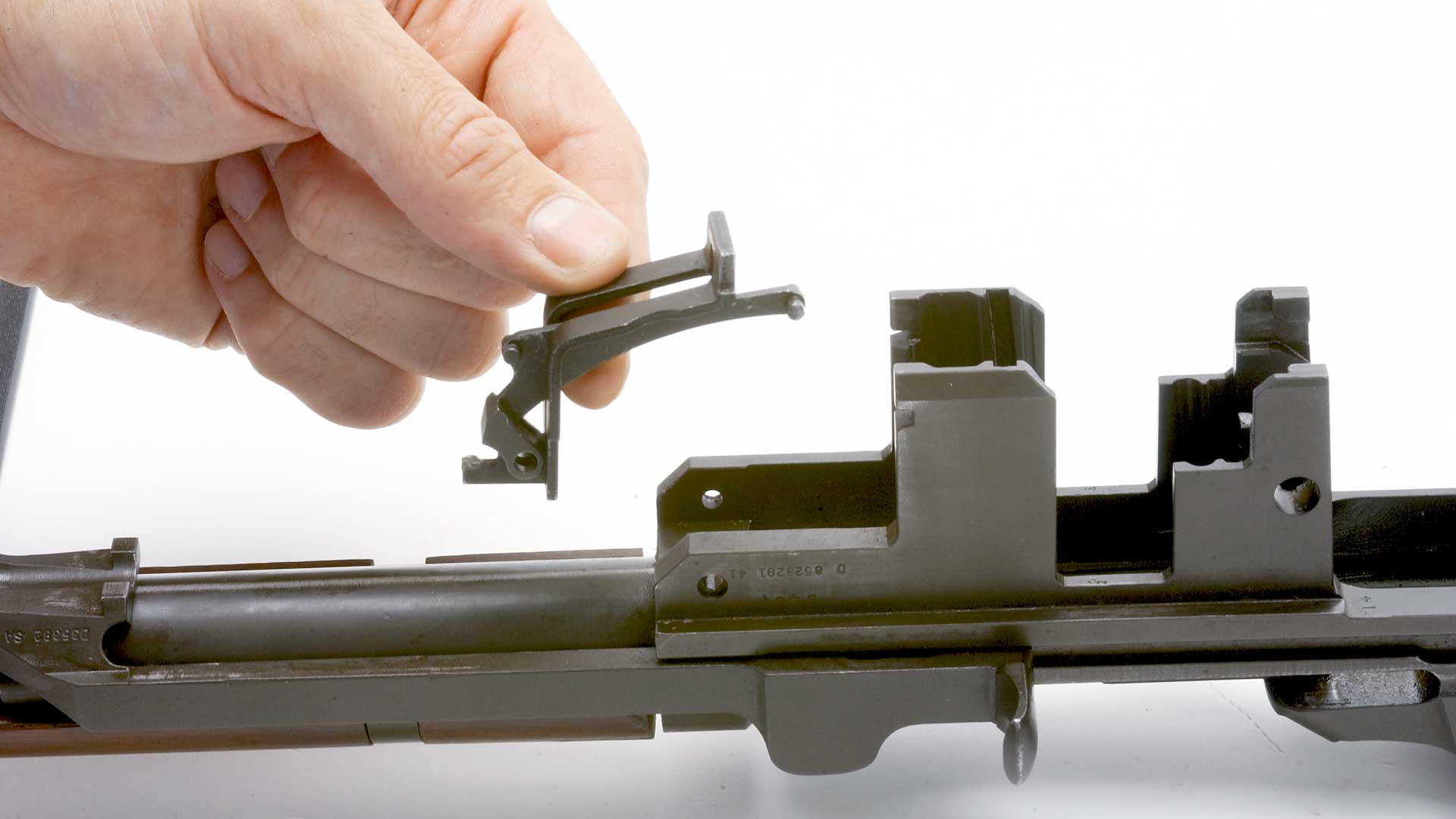

Continue disassembly by pulling the operating rod (38) rearward until the rear surface of the handle is directly under the forward edge of the windage knob on the rear sight. Disengage the guide lug on the operating rod through the dismount notch on the receiver with upward and outward pressure on the handle of the operating rod (Fig. 3). The rod should now come free from the receiver. Remove the bolt (4) by grasping it and sliding it forward while lifting upward and outward with a rotating motion (Fig. 4).
With a large, blunt screwdriver, unscrew and remove the gas cylinder lock screw (30). Unscrew and remove the gas cylinder lock (29). Next, remove the gas cylinder (28) by sliding it forward and off the barrel. If the gas cylinder is tightly attached, rap on the bayonet stud with a nylon hammer or piece of soft wood to loosen it. Do not burr or damage the internal splines. The front handguard (23) may then be moved forward and off the barrel.
This is all that is needed for basic cleaning. All other bolt and trigger housing disassembly and parts replacement should be done by a competent gunsmith. Reassembly of the M1 is in the reverse order.
A few precautions: The operating rod for the M1 has a bend that is intentional, and it should never be hammered on or straightened out. The crown of the operating rod should also be kept bright by using a solvent and nylon brush. Do not scrub with a metal brush or other harsh abrasive. The tolerances within the gas operating system are quite close and nothing should be used that can affect the system.
All operating parts should have a light coat of lubrication except the inside of the gas cylinder. This should be free of carbon deposits and other fouling, but should be kept dry.





































