By the mid-19th century, the British Empire was near its height. At the time, the British infantryman used the highly successful .577-cal. Pattern 1853 Enfield rifle-musket. The Pattern 1853 was a fine example of a standardized rifle-musket, but by the end of the 1860s, new developments in firearms technology made the muzzle-loading rifle obsolete, namely breech loading. By that point, a few European nations had already developed their own viable examples of breech-loading rifles, like the Dreyse needle gun that had been in use by the Prussians since the 1840s. Thus, the British began to develop their own breech-loading rifles to keep up with the global trend.
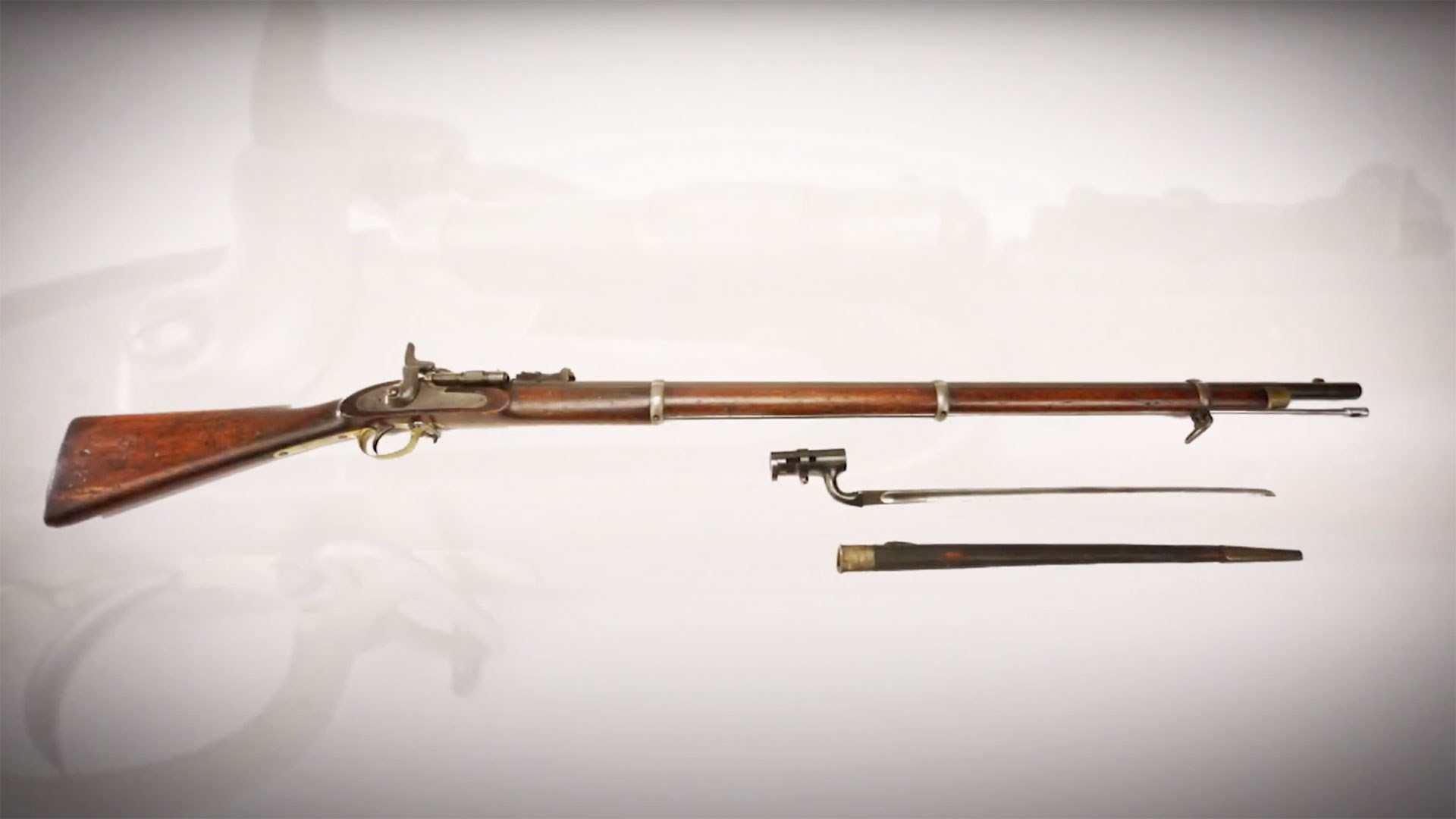 A Sinder-Enfield, breech-loading rifle, which was converted from the older the Pattern 1853 rifle-muskets.
A Sinder-Enfield, breech-loading rifle, which was converted from the older the Pattern 1853 rifle-muskets.
At first, the British developed a stopgap by modifying the actions of existing Pattern 1853 Enfield rifles with breech blocks, allowing the muzzle loading rifle muskets to be converted into Snider-Enfield, single-shot, breech-loading rifles able to accept the new British .577 Snider self contained rifle cartridge. While the Snider-Enfield rifles were well-designed conversions from the Pattern 1853 and allowed the British to spend less, the design had its limitations for accuracy, range and speed of loading. It wasn't long before the British began to develop a purpose-built, breech-loading rifle.
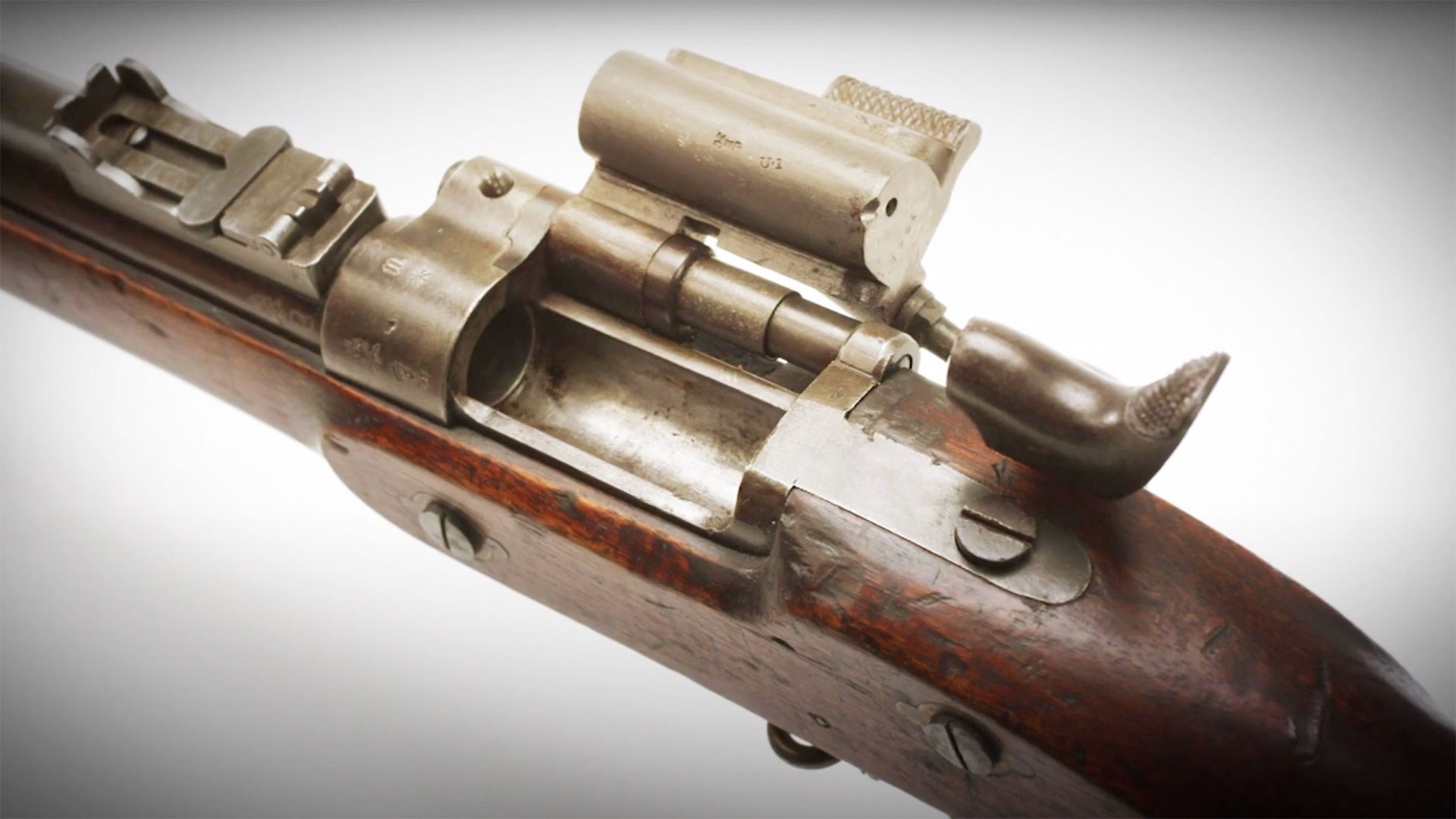 A Sinder-Enfield conversion with the breech block in the open position.
A Sinder-Enfield conversion with the breech block in the open position.
After extensive trials testing different ammunition and action types, the British turned to a falling breech-block design developed by Henry Peabody in 1862, which had been fielded with positive results and improved during the American Civil War. Peabody's pivoting breech-block design was paired with a lever action developed by Swiss designer Friedrich von Martini. New rifling for the barrel was also examined and tested, with a pattern of polygonal rifling developed by Alexander Henry.
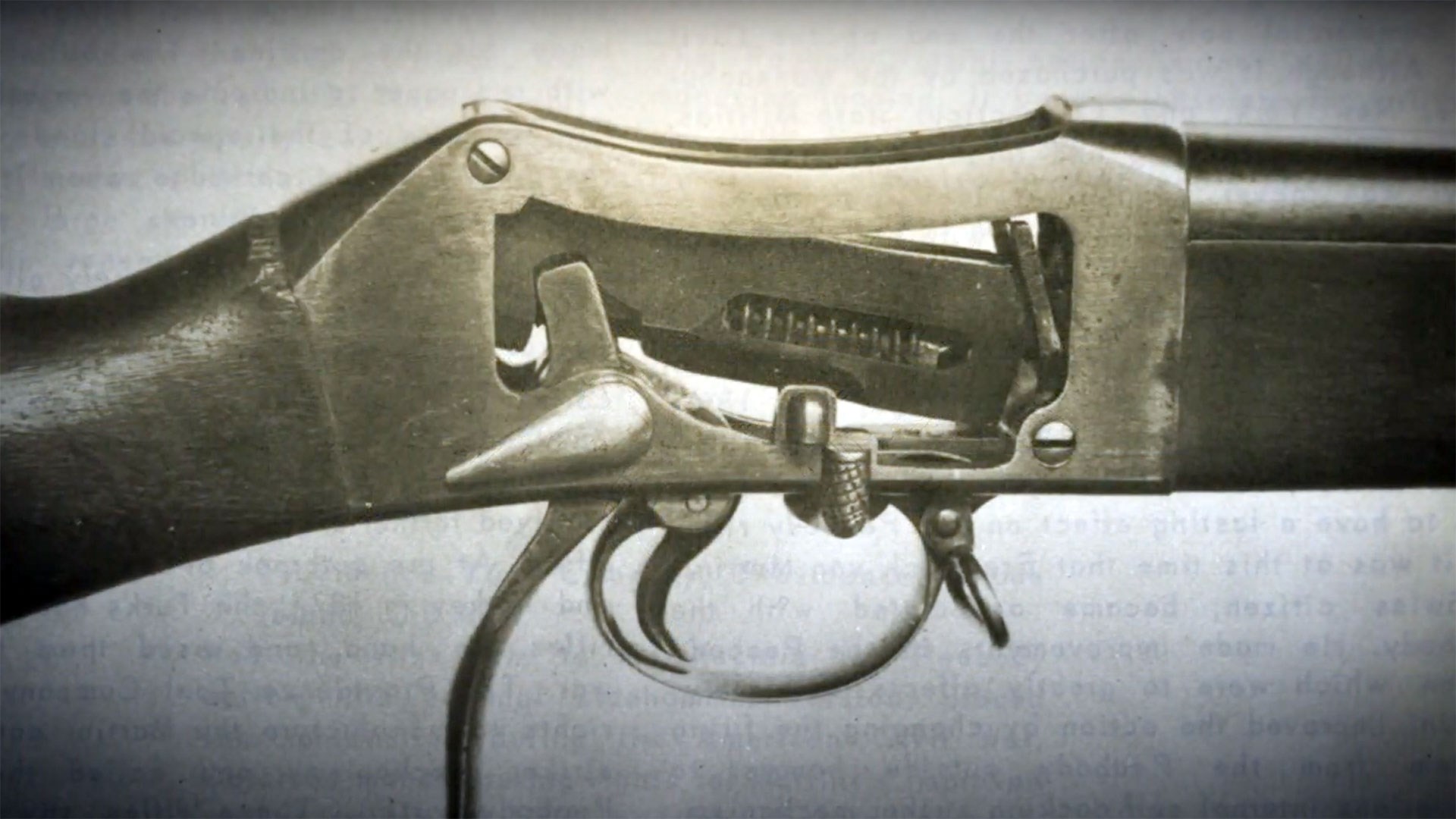 A cutaway example of the Martini-Henry action, with the breech opened.
A cutaway example of the Martini-Henry action, with the breech opened.
The combination of the Martini action with the Henry rifling resulted in the name of "Martini-Henry" for the new rifle design. Adopted in 1871, the Martini-Henry was a streamlined and modern service rifle design for the time. With an unloaded weight of 8 lbs., 7 ozs., and an overall length of 49" for the standard infantry models, the Martini-Henry was large and bulky much like the rifle-muskets that came before it. However, the use of Martini's action and Peabody's bolt design resulted in a smooth receiver profile, with a distinct lever behind the trigger guard and lacking an external hammer.
 Firing a Martini-Henry on the range.
Firing a Martini-Henry on the range.
The Martini-Henrys were chambered for a .45-cal. brass cartridge based on the .577-cal. cartridge that was developed for the Snider-Enfield. The new design quickly became the new standard upon adoption and began to replace the Snider-Enfields, though they would continue to see some service through the rest of the 19th century. Thus, the Martini-Henry became the new symbol of British military dominance, and was used extensively throughout the empire. This famously included the Zulu War fought in South Africa in 1879, where British soldiers used their Martini-Henrys with favorable results.
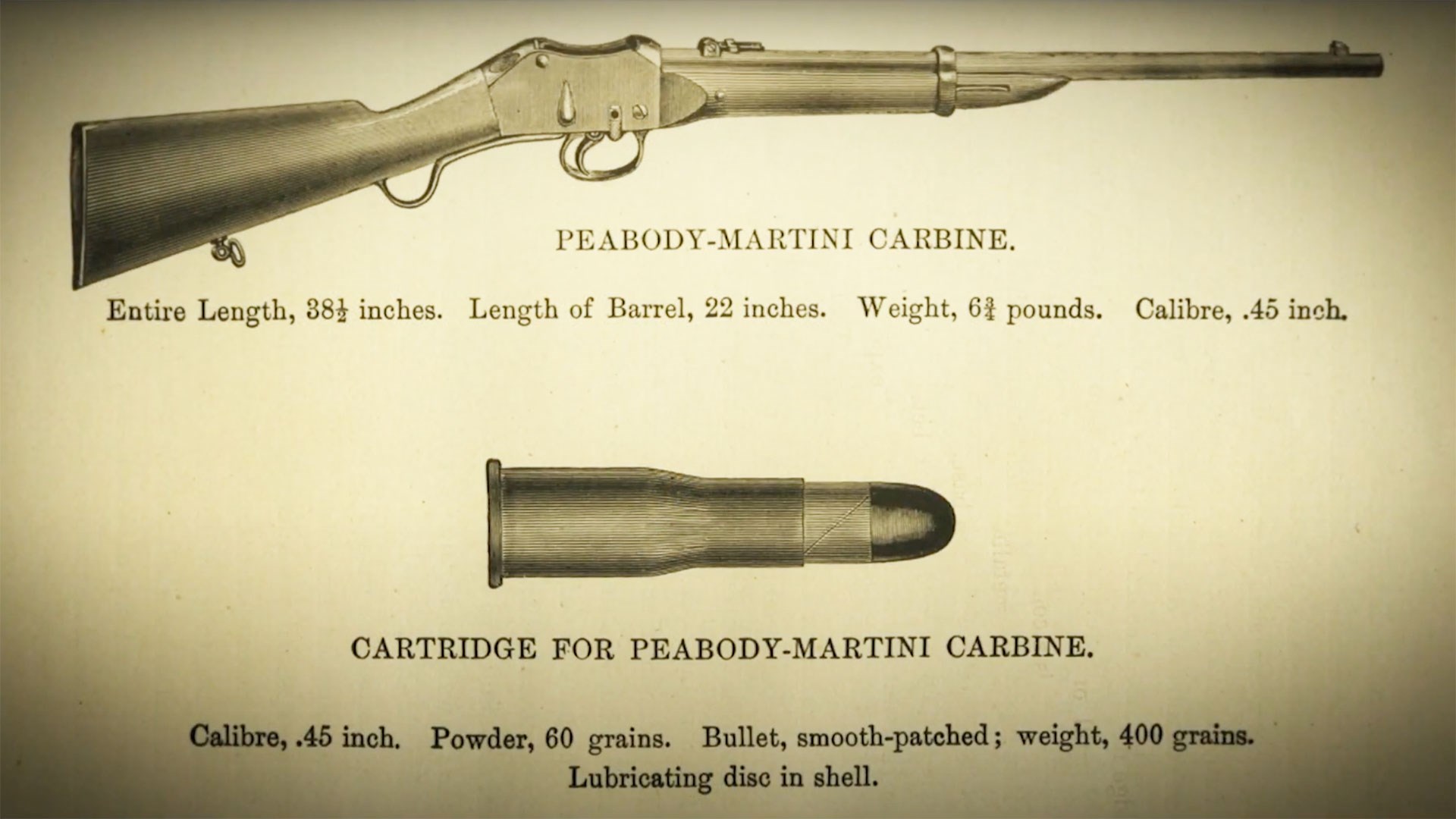 A Peabody-Martini carbine, which was a shortened version over the full 49" long Martini-Henry rifles.
A Peabody-Martini carbine, which was a shortened version over the full 49" long Martini-Henry rifles.
More than half a million of these rifles were made throughout its production, with four different "Marks," or versions, as well as a carbine variant. Its dominance was short lived, however, as the dawn of the bolt-action era quickly made the single-shot breechloaders obsolete. The Martini-Henry was replaced by the Lee-Metford design in 1889, though many Martini-Henrys would continue to be used in reserve in Britain and across the commonwealth up to the end of World War I. Some Martini-Henry rifles were even converted to the .303 British cartridge for reserve and training purposes, which can still be found and used today.
While its service life wasn't as long as the Lee family that succeeded it, the Martini-Henry is a unique design with a distinct profile unto itself, and has grown to represent what was arguably the height of the British colonial period at the end of the 19th century.
To watch complete segments of past episodes of American Rifleman TV, go to americanrifleman.org/artv. For all-new episodes of ARTV, tune in Wednesday nights to Outdoor Channel 8:30 p.m. and 11:30 p.m. EST.
























