Through simple mathematics, everyday shooters, hunters and techie enthusiasts alike can matter-of-factly produce answers to complex questions related to firearms and the ballistics therein. The following formulas and tables had been produced in previous NRA publications. For more comprehensive study, check out the NRA Firearms Sourcebook at your local library, or visit your NRA Store website.
Break out the paper and pencil; this is where things get nerdy.
STANDARD DEVIATION
Statisticians rely on standard deviation (Sd) values to monitor the amount of variation from the average. Calculated Sd values from velocity readings are often used during the study of ballistics. Target shooters and hunters, and especially handloaders make note of these values during ammunition selection. Gunsmiths use the Standard deviation formula as well. Standard deviation computation is easily done with modern devices. The old fashioned way will get you through when the power goes out. Here is how:
Step 1—Determine average velocity of all shots (or distance from the center of the group). Use as big a sample as possible (typically 20 shots).
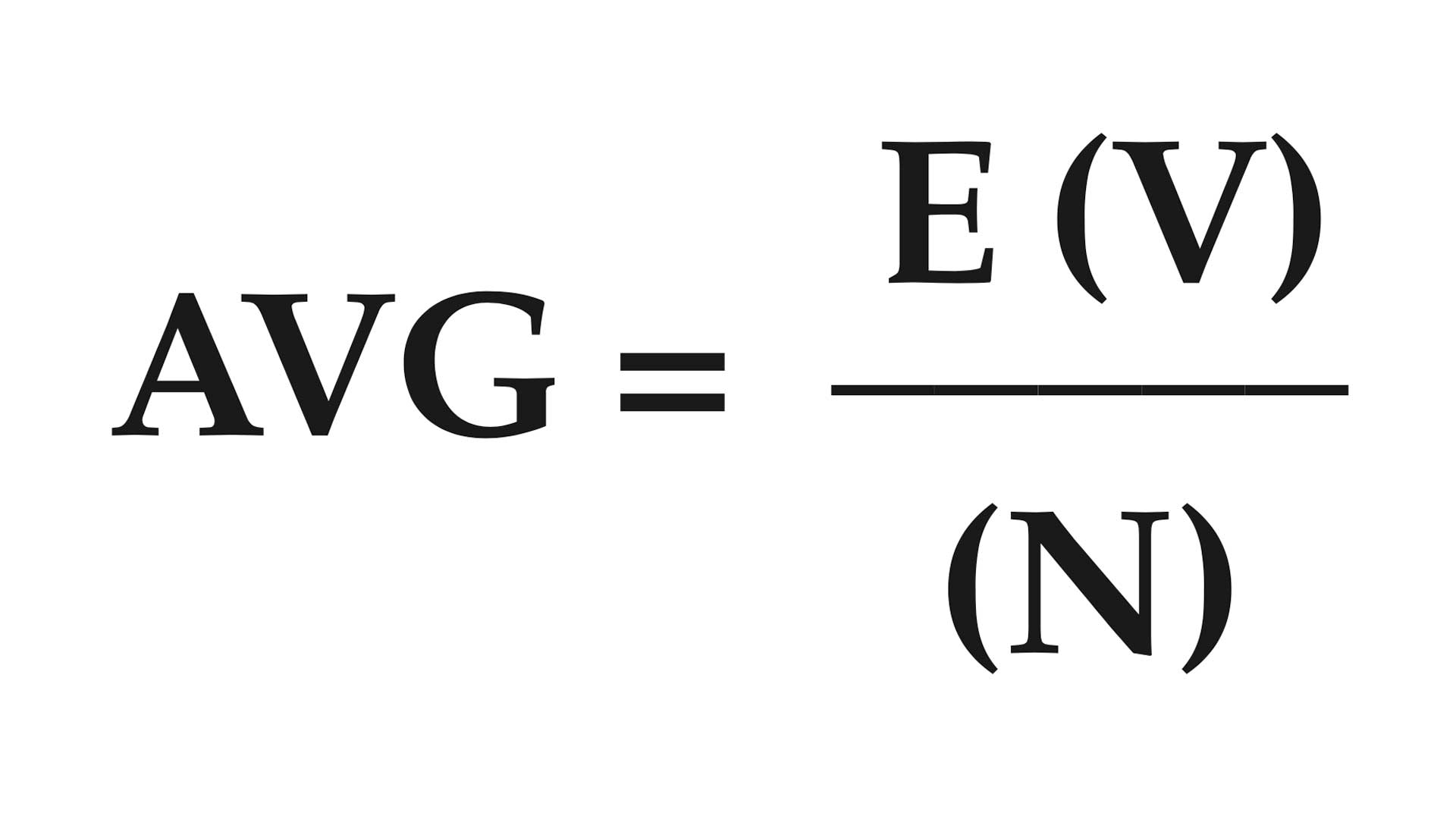
AVG = average velocity or distance
V = velocity or distance of each shot number of shots
N = process of successive addition
E = (add velocities or distances together)
Step 2—Find the difference between each shot and the average. Square each result and add together. Divide by number of shots minus one.
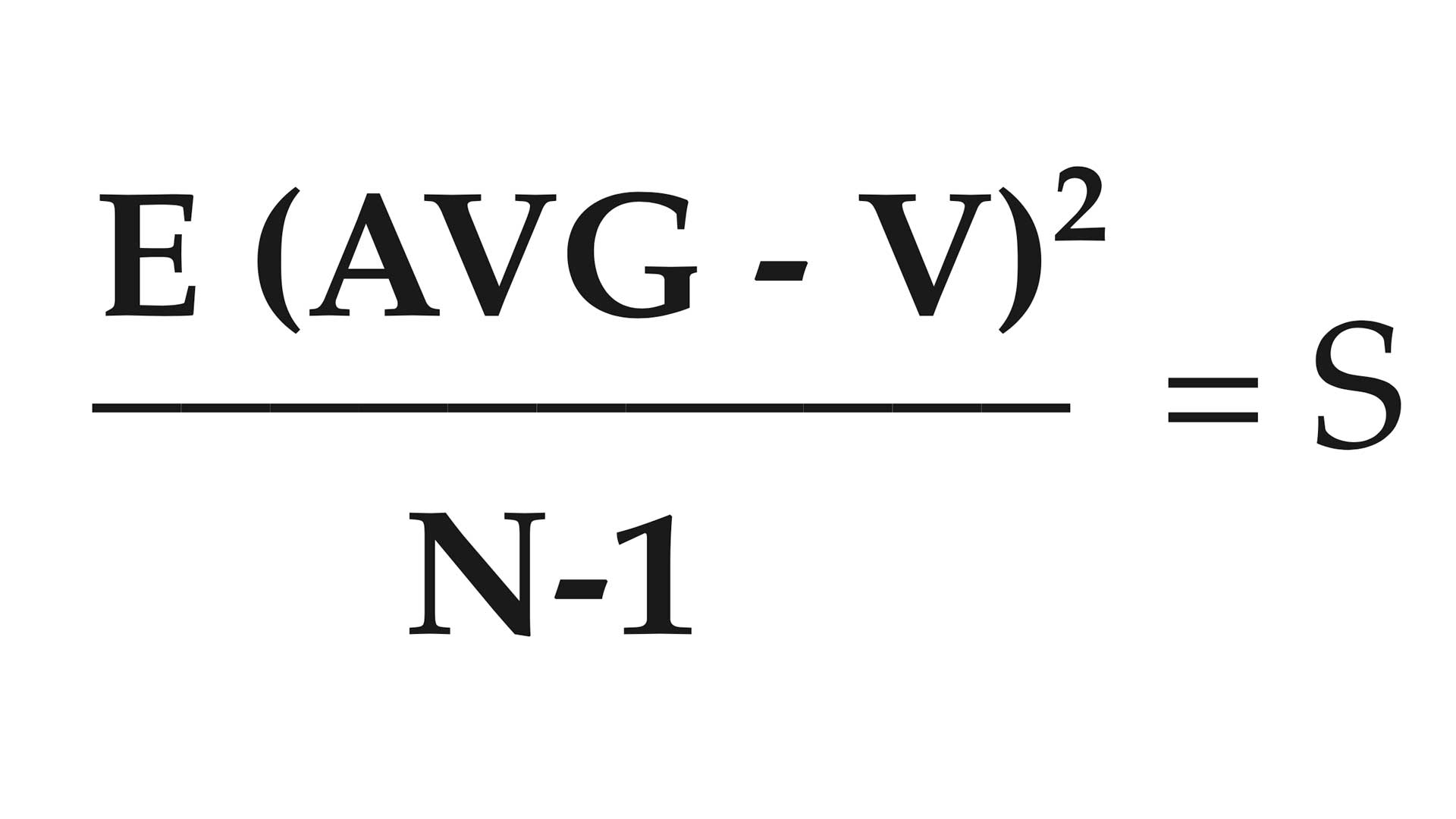
AVG = average velocity or distance
V = velocity or distance of each shot
N = number of shots
E = process of successive addition (add squared results together)
Step 3—Take the square root of the results of Step 2.
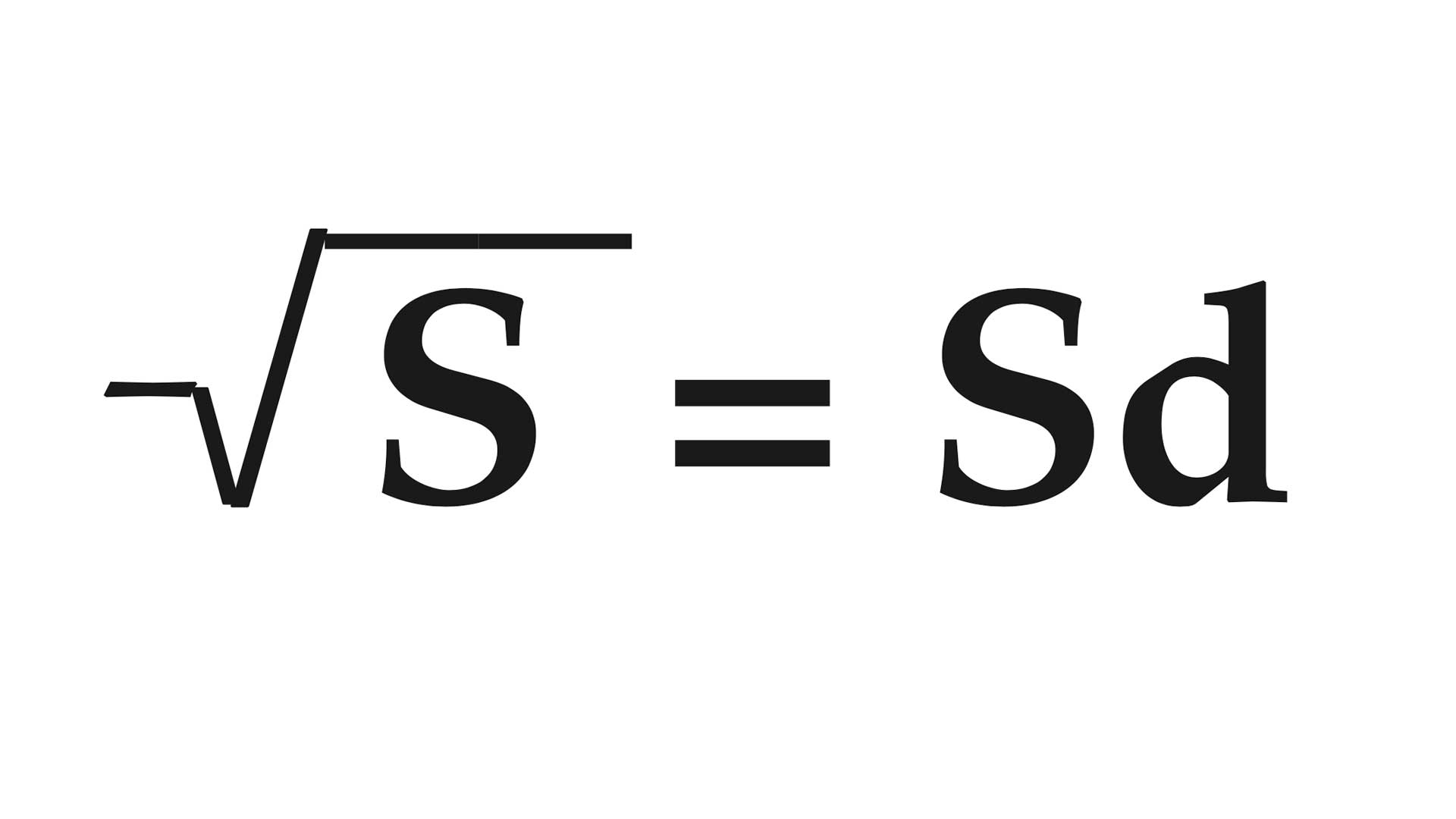
S = Step two result
Sd = standard deviation
EXTREME SPREAD OF SHOTS
Understanding the extreme spread within a set of values is useful to all shooters. Extreme spread, in terms that relate to target accuracy, measures precision of shot group. The following formula will pinpoint accuracy nodes recorded during formal range work.
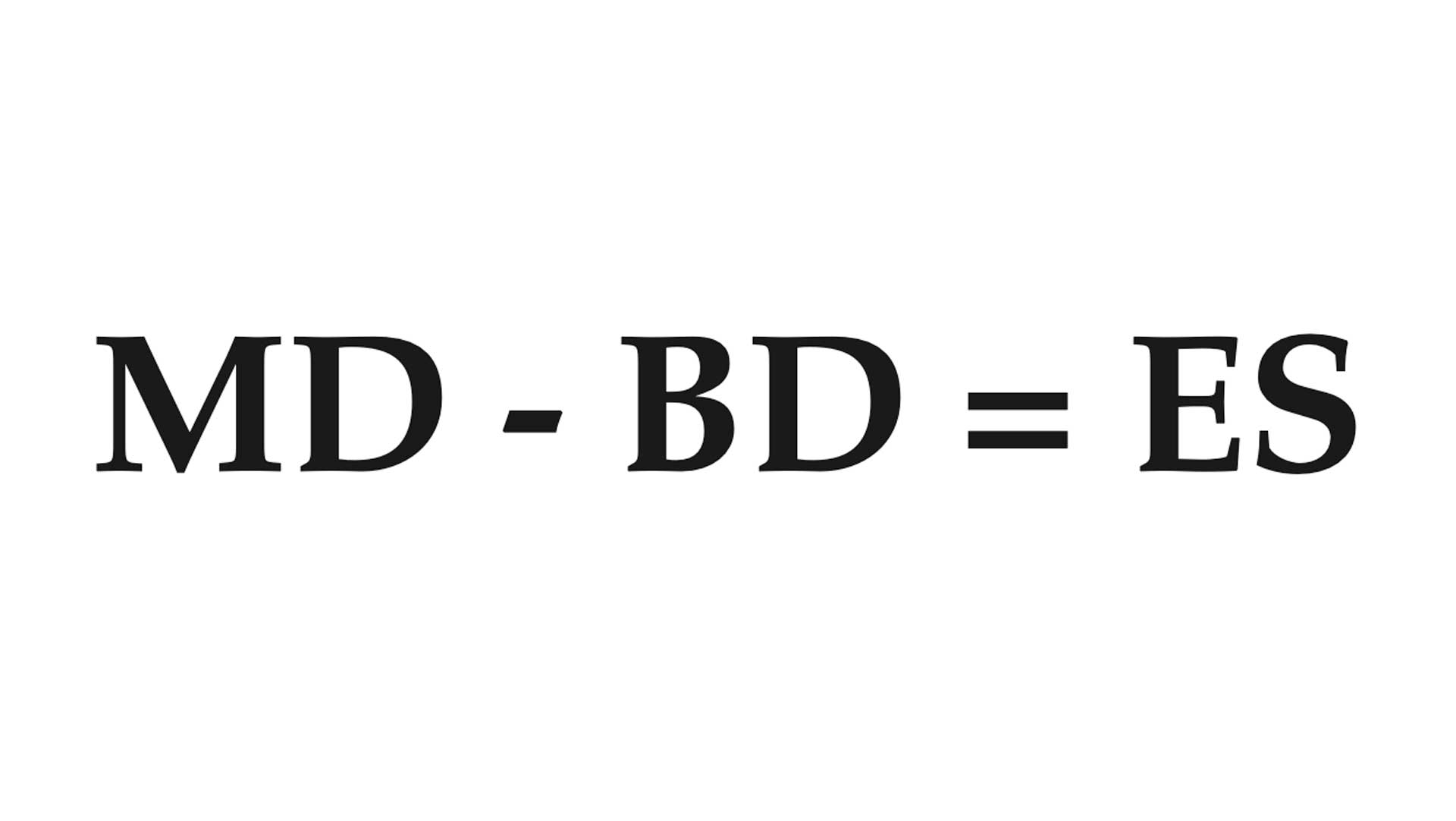
MD= maximum distance between the most widely separated shots
BD = diameter of bullet
ES = extreme spread of shot group
American Rifleman accuracy testing protocol for pistols, handguns and rifles requires extreme spread calculation following five, five-shot groups. Rimfire-cartridge guns call for five, 10-shot groups and shotgun data is sampled from 10 shots.
MEAN VERTICAL OR HORIZONTAL DEVIATION OF SHOTS
The average horizontal or vertical distance from the group center of impact is factored by the following formula:
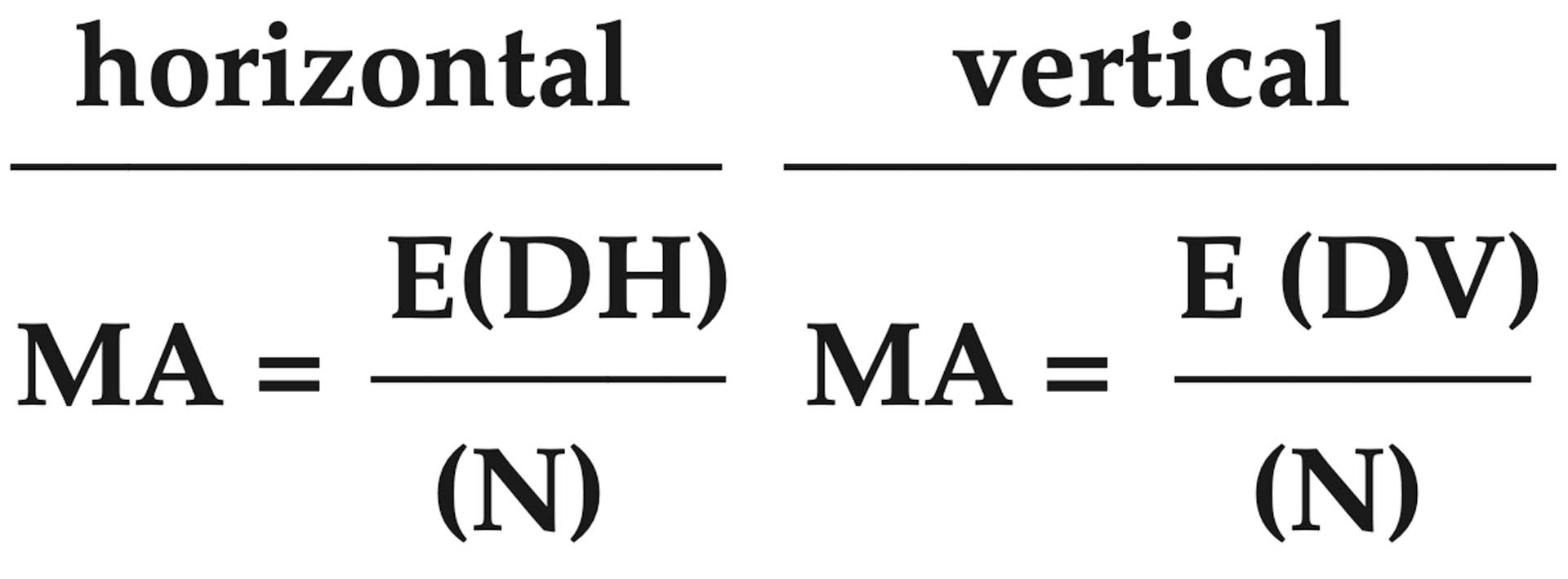
MA= arithmetic mean measure of central tendency
DH = horizontal distance of each shot from center of impact of the group
DV = vertical distance of each shot from center of impact of the group
N = number of shots
E = process of successive addition (add distances together)
MAXIMUM MEAN RADIUS OF SHOTS
The average of all radial distances from the group center of impact.
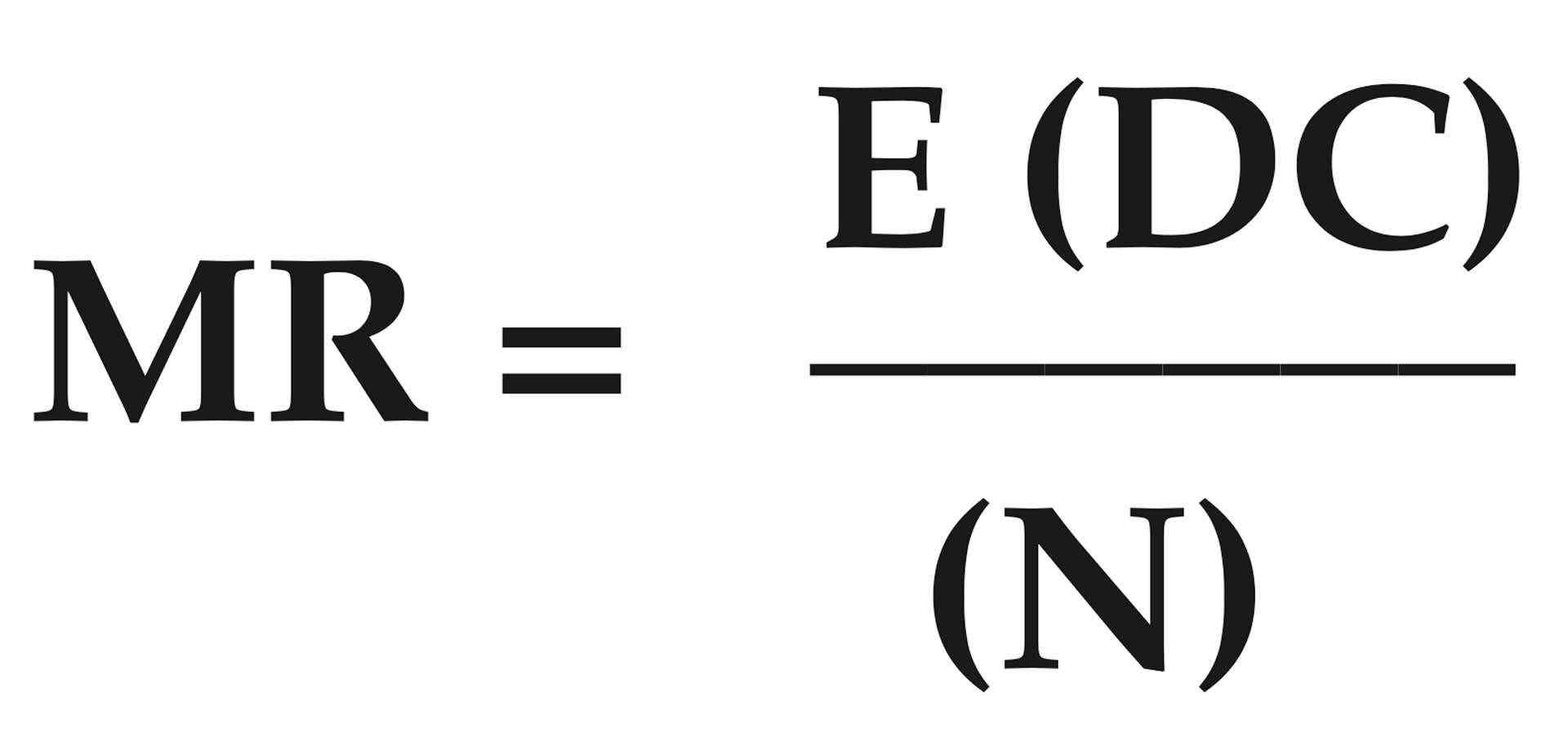
MR = maximum mean radius
DC = distance of each shot from center
N = number of shots
E = process of successive addition (add distances together)
BULLET STRIKING ENERGY
The striking energy of a bullet in foot-pounds (ft.-lbs.).
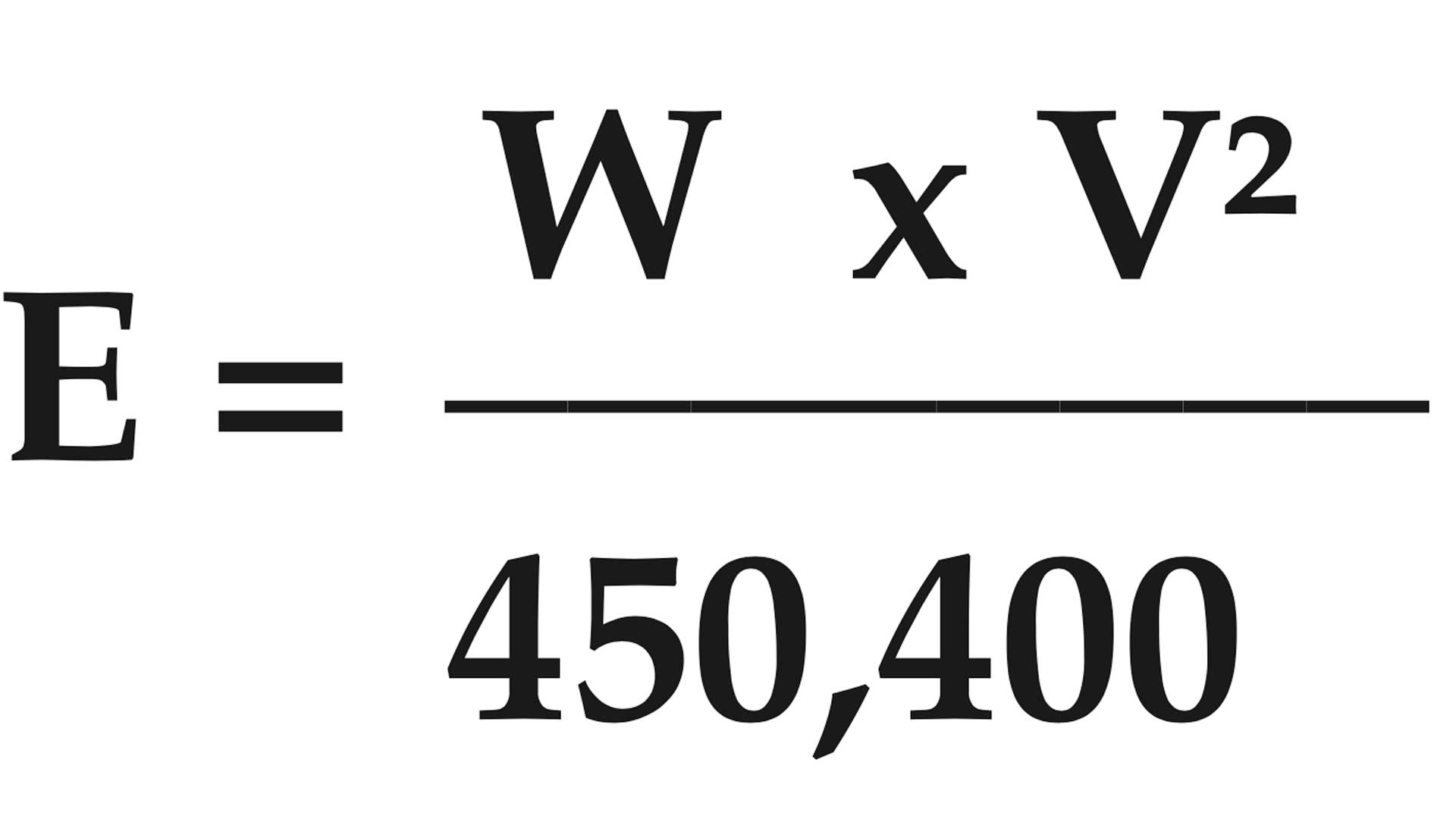
E = energy of bullet in ft.-lbs.
W = weight of bullet in grains
V = velocity of bullet in feet per second (f.p.s.) squared
BULLET STRIKING MOMENTUM
The impetus of the bullet as it strikes the target.
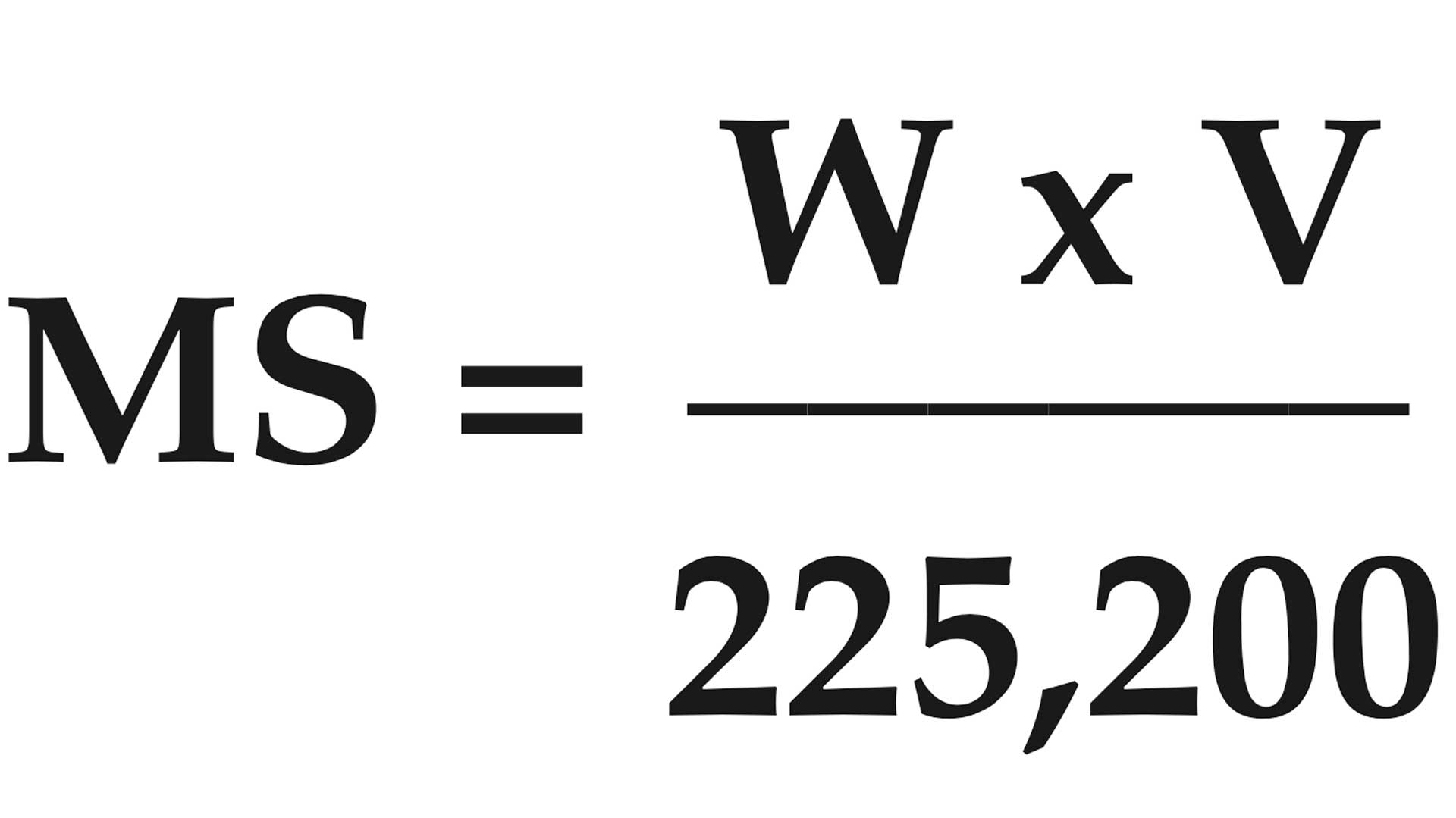
MS = striking energy in lb.-sec.
W= bullet weight in grains
V = striking velocity in f.p.s.
BULLET WIND DRIFT
Determines horizontal displacement of bullet at target due to 90 degrees crosswinds.
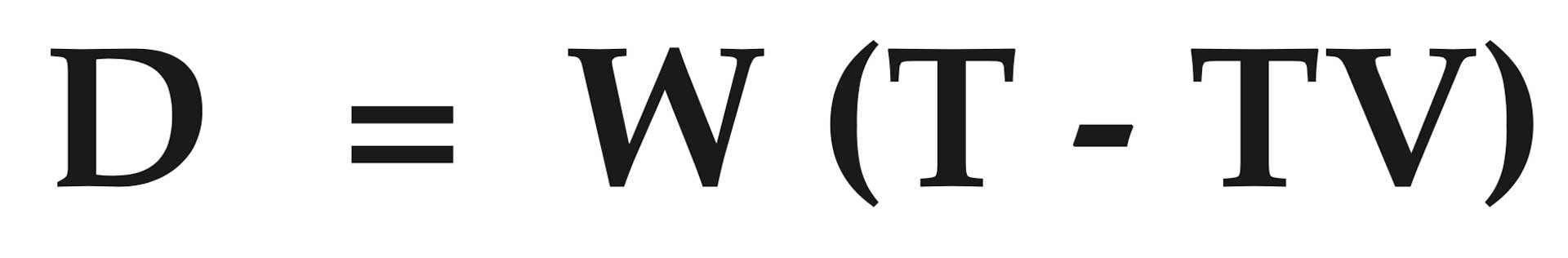
D = W (T - TV)
D = wind deflection in feet
W = crosswind velocity in f.p.s.
T = bullet’s time of flight to target in seconds
TV = bullet’s time of flight to target in vacuum in seconds (range to target in feet divided by muzzle velocity in f.p.s.)
BULLET TIME OF FLIGHT
The time in seconds it takes for a bullet to travel from the muzzle to the target.
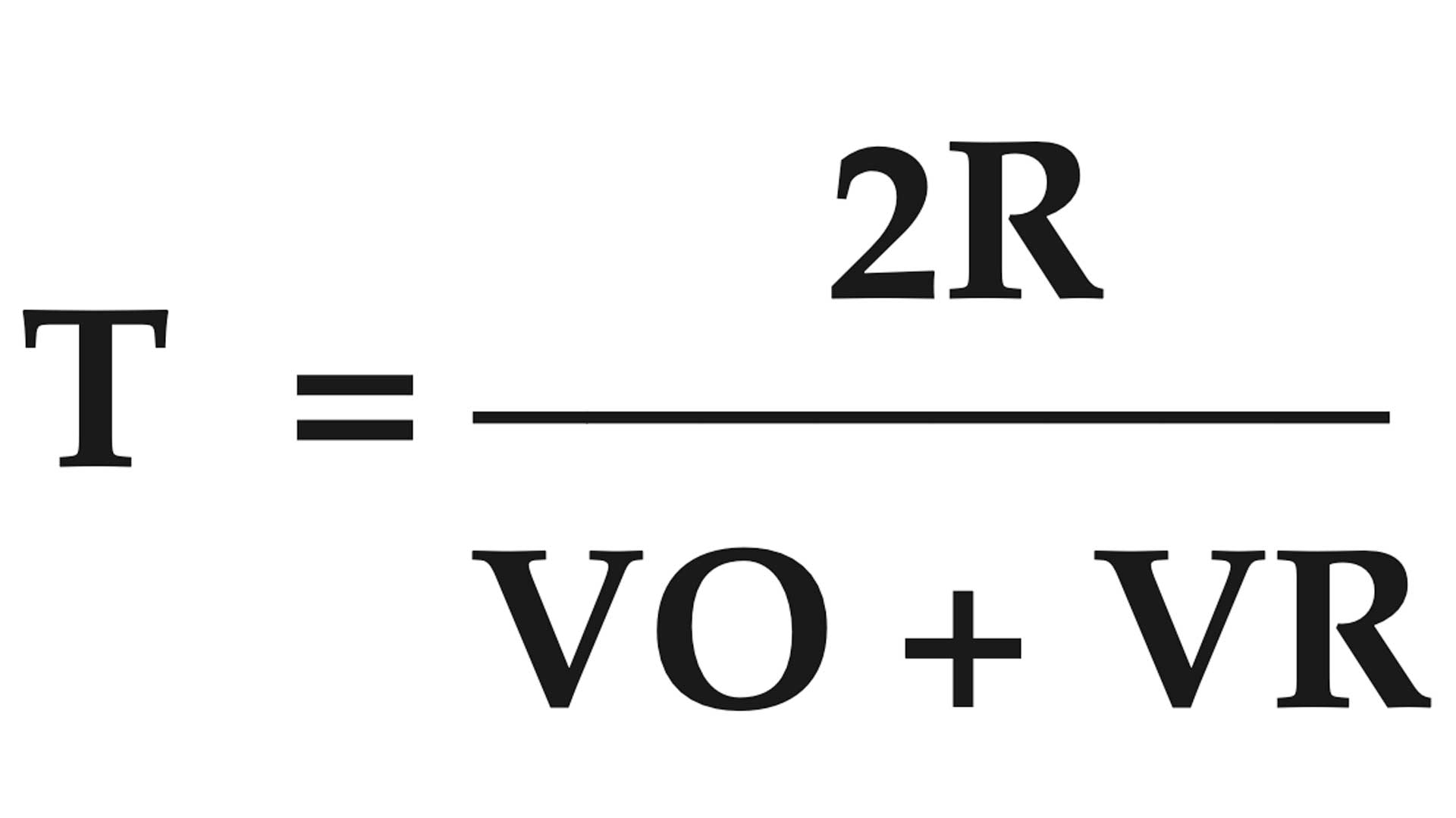
T = bullet time of flight in seconds
R = range to target in feet
VO = muzzle velocity in f.p.s.
VR = remaining velocity at target in f.p.s.
BALLISTIC COEFFICIENT OF A BULLET
The ratio of a bullet’s ability to overcome air resistance and maintain velocity compared to a standard.
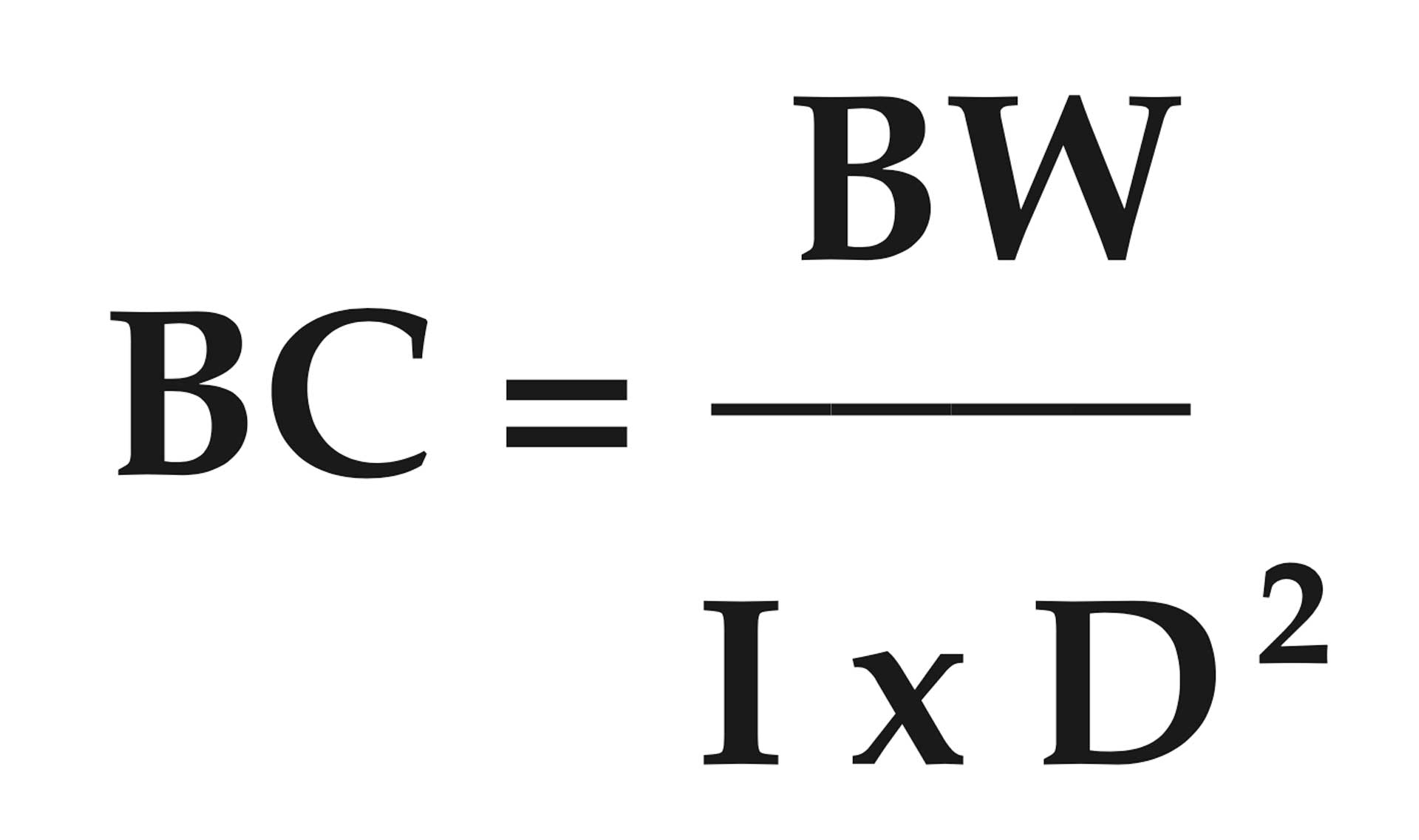
BC = ballistic coefficient
BW = bullet weight in pounds (bullet weight in grains divided by 7,000)
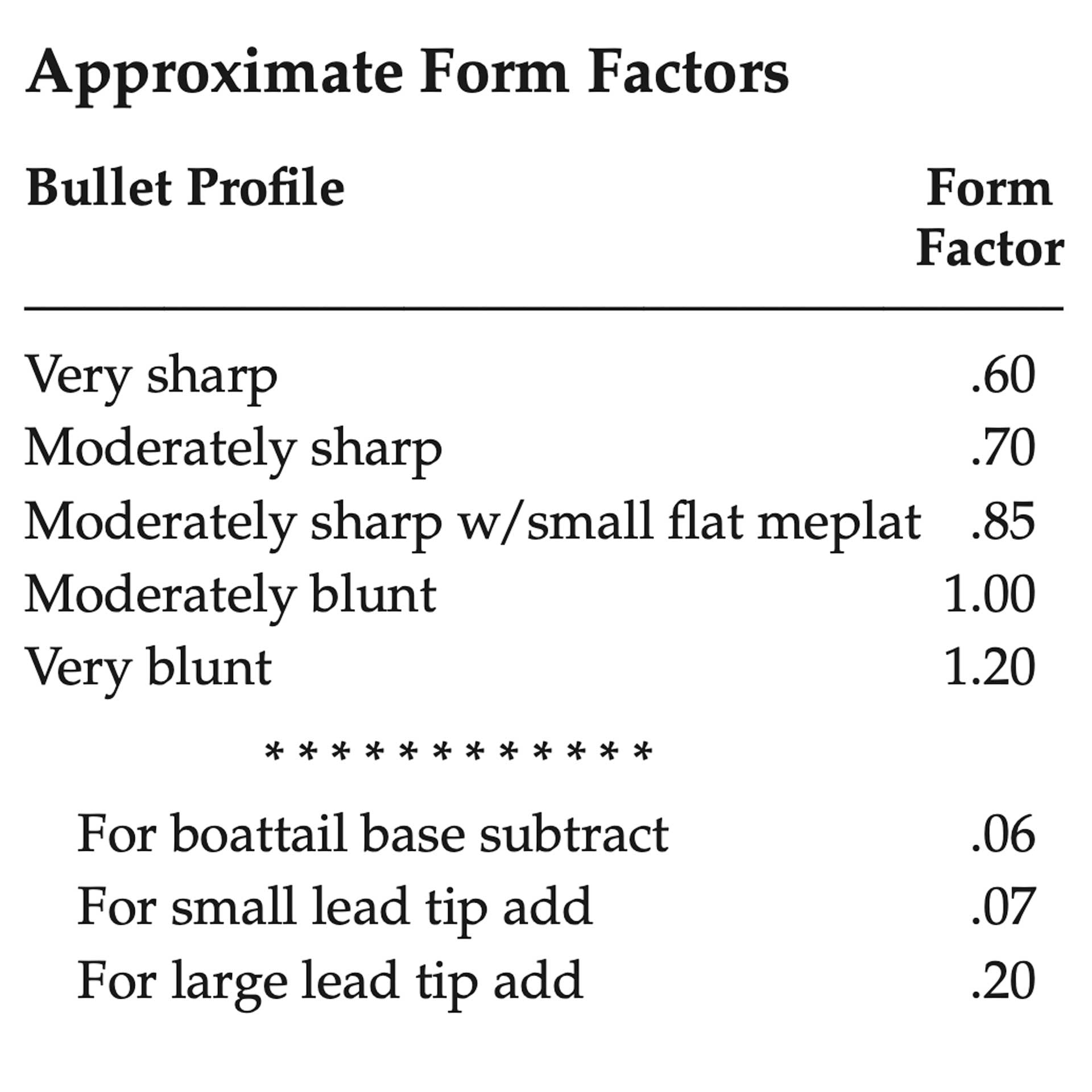
I = form factor of bullet (see chart below)
D = bullet diameter in inches
SECTIONAL DENSITY OF A BULLET
The ratio of a bullet’s mass in pounds to the square of its diameter.
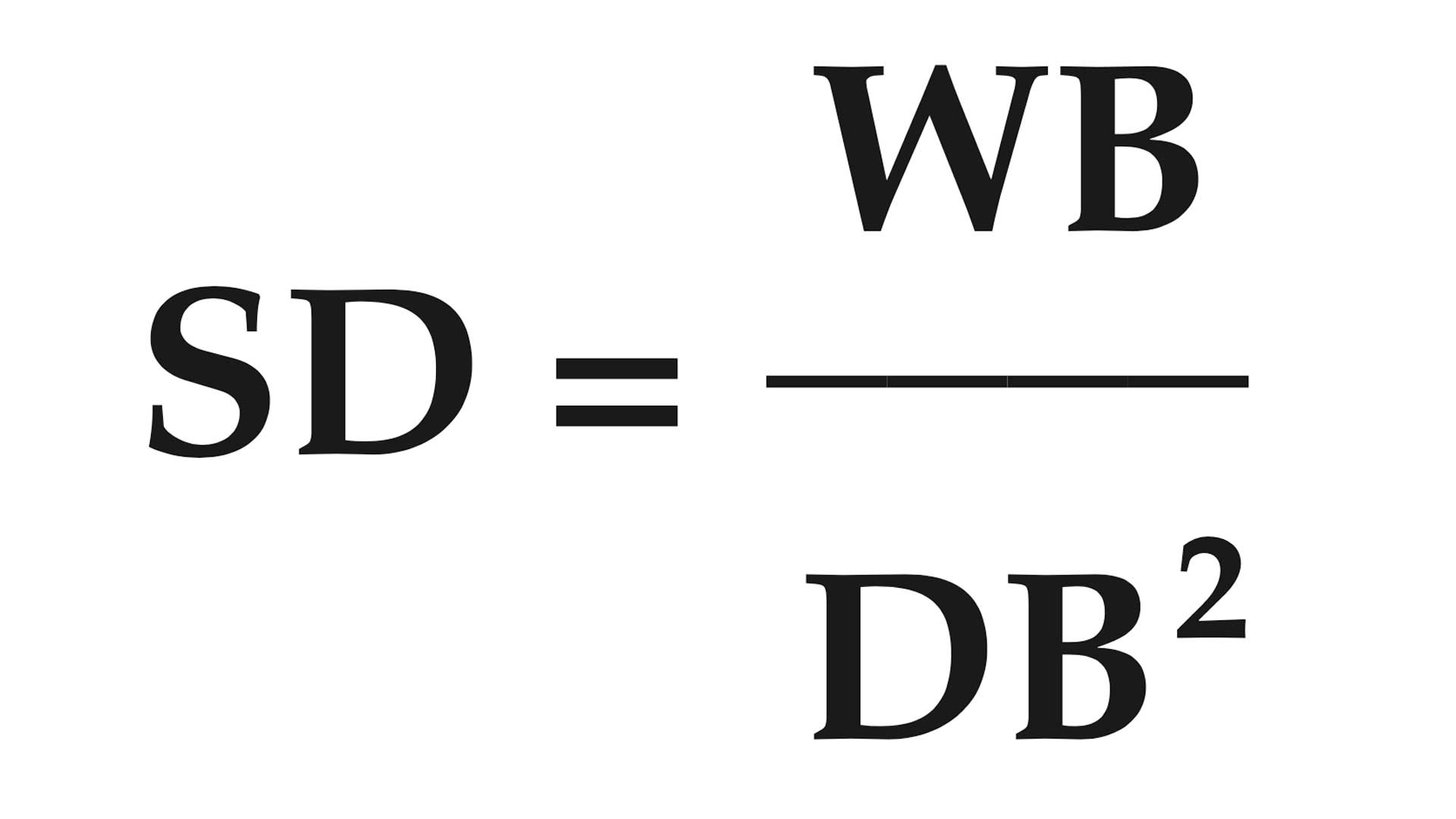
SD = sectional density of bullet
WB = weight of bullet in pounds (weight in grains divided by 7,000)
DB = diameter of bullet in inches squared
DRAM EQUIVALENT
A dram is an English unit of weight equal to 1/16 of an ounce or 27.3 grains.
Drams were the standard unit of weight measurement for loading shotguns with blackpowder before smokeless powder became common. Today, the performance potential of smokeless-powder shotshell loads are frequently expressed in dram equivalents. Unlike blackpowder, this is not a measure of powder charge weight. Rather it is a gauge or guide to indicate the approximate muzzle velocity of a shot charge of a given weight propelled by smokeless powder in blackpowder performance terms. Dram equivalent numbers are therefore not direct conversion factors for loading smokeless powder shotshells.
Examples:
1. 12 ga.-2 3⁄4"- 3-dram-equiv. 1 1⁄8-oz. shot, muzzle velocity is 1,200 f.p.s.
2. 12 ga.-2 3⁄4"- 3 3⁄4-dram-equiv. 1 1⁄4-oz. shot, muzzle velocity is 1,330 f.p.s.
Stay tuned to AmericanRifleman.org to learn more "Formulas For Success."



































